Conformation
and Selection for Performance
By Don Blazer
Copyright © 2003
What a
horse does best is move.
His efficiency of movement is the foundation
of his survival, his evolution, his beauty and his grace.
By all accepted standards, what we say
is "good conformation" is said specifically as it relates to the
horse’s efficiency of movement.
If our desire is efficient movement, then the
ideal conformation is the form which best achieves efficient movement. And by
its very nature, it is also the form which most assures, BUT DOES NOT
GUARANTEE, continuing soundness.
But efficiency of movement is not
always what we want.
Various breeds accentuate certain
conformational traits which affect movement, and particular performance
disciplines demand distinctive variations of movement. So the desire for
efficiency of movement is replaced by another desire. The new movement desired
always subjugates efficiency. And over a period of time the various desired
movements result in conformational changes. The changes in themselves are not
necessarily right or wrong; they are simply choices. But all choices which
limit natural efficiency of movement come with consequences.
Click on the following link to see a
“quick conformation overview”. This is a
standard conformation report that does not relate form to specific function, a
task you will be asked to do at the end of this lesson.
http://muextension.missouri.edu/explorepdf/agguides/ansci/g02837.pdf
Understanding a horse’s conformation,
and the deviations from the established standard, allows you to recognize how
and why a particular horse moves as he does. And with that understanding you
can choose the performance work most suitable for that individual.
But before we begin our observation of
specific conformation traits and their affect on performance, I want to review
some basics of horse identification and reference. Click on the link to view the
information. (If you have a slow server
– be patient – the graphics may take some time to download.)
There are two ways to judge a horse’s
conformation.
One: determine the correctness of the
form as it relates to efficiency of movement. (This is supposedly how halter
horses are judged--form as it meets the breed standards. Halter horses of any
breed seldom reflect efficiency of movement, instead portraying the
"beauty" of the current fad, which is correct if meeting the
standards of a new desire.)
Two:
determine the strengths and weaknesses of a particular conformation as it
relates to the performance desired. (Selective breeding has been successful in
producing horses with both conformation and talent for specific exercises.
Knowing what performance you want from a horse allows you the opportunity to
select by breeding, the natural desire to work, and by conformation, the
natural ability to work.)
Always keep in mind that a horse’s
action is initiated in the hindquarters. The hindquarters is
the power plant of the horse, the driving force. The forehand catches,
rebalances and stabilizes the horse. The conformation you are seeing (forehand,
hindquarters, overall) should be evaluated either in relationship to how well
it can function in performing the desired movement, or for its contribution to
efficiency of movement.
View a horse’s conformation from three
positions "directly in front of the horse, at the side of the horse and
directly behind the horse. Looking at the horse head-on allows you to see the
width of the forehead, the chest and the alignment of the front legs. Looking
at the horse from the side allows you to view the set of the head and neck, the
top line, the underline and the positioning and angle of the legs. Standing
directly behind the horse you can see alignment of the hind legs, the level of
the hips and the straightness of the spine. (To fully see the spine, it may be
necessary to stand on a platform to elevate your view.)
Conformational Balance
Balance is the overall symmetry of an animal and is
one of the most important of the evaluation criteria. Balance is evaluated by viewing
the profile of the animal. When viewing the horse, his body should appear
symmetrical with all of his parts blending smoothly together. There are several
ways to evaluate balance and these are illustrated in the following diagrams.

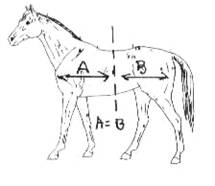
A well-balanced horse can be divided into two equal halves. Although not the most common method, many beginners can visualize "halves" better than thirds. A horse should not appear more massive in the forehand than in the hindquarters (or vice versa). Rather a horse with a well-developed forehand should have well-developed hindquarters to match.
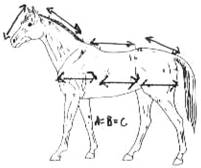
This illustration depicts the more common and more correct way to evaluate balance.
A horse that is balanced should have lengths of
head, neck, top line and hip that are nearly equal. Similarly, a balanced horse
can have his body divided such that the lengths from the point of the shoulder
to the barrel (a), from the barrel to the point of the croup (b), and from the
croup to the point of the buttocks (c), are equal.
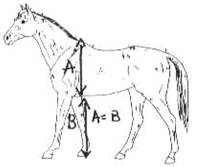
In addition to balance from head to tail, a well-balanced horse should have a similar distance in the girth (a) as from the underline to the ground (b). Horses which appear shallow-hearted, or to have extremely long legs are not considered well balanced.
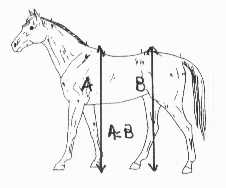
The final consideration in evaluating balance is
determining how level the horse is over his top line. A balanced horse is similar in height from the
ground to the withers (a) as from the ground to the croup (b). A horse that is higher in the forehand or
higher in the croup is not well-balanced.
Generally, a horse with a long-sloping shoulder will have a short top line. A short top line is desirable because shortness denotes strength of top, and a top line that will withstand the stresses of riding. Note the difference between horses with strong and weak top lines.
When viewing a horse for strength or correctness of the top line, the top line should appear relatively short in comparison with the animals underline. Horses long in the loin will appear to have top lines and underlines of similar length.
ANGLES
Use this skeleton of the horse to more easily see the angles created by the joining of bones. For example, there are two lines through the scapula…if you follow the ridge of the scapula you get an angle close to 45%…this would be the perfect angle of the shoulder for efficiency of movement. However, if you follow the line through the joint of the scapula and humerus, you will get an angle closer to 50 degrees.
The skeleton shown is drawn to be a perfectly balanced horse with maximum efficiency of movement. Seldom do we see such a horse.
Click here to view the skeleton.
FEET
If I am looking at a horse for
possible purchase, I will stand in front of the horse and look at the coronet
bands of both his front and hind feet. I want to see an even coronet band,
symmetrical with the opposite one. The coronet band should flow across the
front of the foot and should not have dips or upward variations. The hair line
should move evenly around toward the heel and should not sink down toward the
ground. Any deviation in the hair line at the coronet band tells you there is
something going on of concern.
Keeping the coronet band as the main focus, I
can view the entire hoof. I look for flares, differences in the angle of the
medial and lateral hoof wall, pulled in heels and hoof wall damage.
Moving to the side of the horse I look for
dorsal/palmar (front to rear) balance. Determine if
the horse has a broken forward or broken backward hoof/pastern axis. Carefully
analyze the angle of the hoof wall horn, noting any tendency toward under-run
heels.
I then pick up each foot and look at the
medial/lateral balance, the condition of the frog, the medial/lateral heel
lengths, the position of the bulbs of the heel, and the width of the heel.
A horse with small feet can do just about
anything, but his soundness will be questionable, especially if he is asked to
work in high impact events.
Flat footed horses should be worked only on
soft footing.
Mule feet are narrow with steep walls. A horse
with mule feet should be worked only on soft footing.
Coon footed means the horse has a very upright
foot, while the pastern slopes radically toward the hindquarters.
Club feet are defined as a foot with high
heels and a front face which exceeds 60 degrees. Club feet can be genetic,
caused by the horse having one leg shorter than the other, or faulty
nutritional practices with young horses.
Contracted heels and small frog are common
results of poor shoeing practices. Horse with such problems should be used only
in non-concussion events.
Narrow hoof walls predispose the horse to sore
feet and are often associated with flat feet.
Without a foot, the rest of the horse’s
conformation matters little. If the horse has too many obvious foot problems, I
don’t have an interest in purchasing him. While most foot problems are the
result of poor care and/or poor shoeing, many will be associated with
conformational faults.
If I have been asked to evaluate the horse, I
simply note my observations of the hoofs and move on.
HEAD
Return to a position in front of the horse and
study the horse’s nostrils. I want to see a large nostril, capable of opening
wide to allow maximum air flow. A great air supply is extremely important to
any horse which will be used in activities requiring speed and stamina. (Racing, cutting, jumping, eventing.)
The more air a horse gets into his lungs, the
more oxygen the blood carries to the muscles, having a direct effect on the
horse’s ability to perform.
A horse with small nostrils should be considered
for pleasure riding or trail.
It is best if the horse’s face is
neither dished nor bulged out. A smooth, straight line from a point between the
ears down the nose to the nostril allows air flow. A dished face is a major
restriction to air flow and severely limits the horse’s ability to perform with
speed or stamina. A bulging face line (Roman nose) interferes with the horse’s
ability to see clearly and is usually associated with horses of poor
temperament, willfulness or spookiness.
A large, soft eye set to the side of the head
generally allows the horse to see well, and is associated with a horse of kind
temperament. Small eyes, often called pig eyes, restrict a horse’s vision. The
horse has both monocular and binocular vision. He can look at two different
things at the same time, or he can use both eyes to concentrate on a single
point, so what he sees can be quite distracting to him. In addition, the retina
of the eye doesn’t form a perfect arc, so the horse must frequently shift his
head position to bring particular observations into focus.
It is not advisable to have the eyes set too
far to the side of the head, as this causes the horse even more trouble
bringing things into focus. It is also much more difficult for the horse with
wide-set eyes to focus both eyes on a single object, which in turn limits his
ability to concentrate.
A horse with a well defined jaw line usually
has a relatively wide jaw, which is an asset. Make a fist and place it between
the horse’s jaw bones at the throatlatch. A horse of one year or older will
have what is considered a wide jaw if you can slide four knuckles of your fist
between the jaw bones. This width allows for good air flow.
With width between the jaw bones, the
throatlatch will be clean and well defined. A well defined throatlatch is
important since everything essential to the horse’s performance--blood, nerve
impulses from the brain, air--travels through this area.
Horses which are narrow between the jaw bones
should be directed toward performances not associated with speed or endurance.
NECK
The neck is measured from the poll to the
withers and should be about one-third the length of the horse’s body measuring
from the tip of the nose to the buttock. The neck should be set on the horse’s
chest neither too high, nor too low, but aligned for forward movement.
A short neck does not affect the length of the
horse’s stride, does allow for quick air flow to the lungs, and does aid in the
horse’s ability to make quick changes of direction. A short neck is not considered
advantageous for a jumper or for a horse expected to work with speed for long
distances. However, a horse with a short neck gets plenty of air to sprint and
will usually have the lateral agility needed to cut cattle.
A long neck causes the horse to be heavy on
the forehand, but is acceptable in jumpers and horses working in straight
lines.
An upside down, or ewe neck relates to high
head carriage and compromises all performances. A horse with the upside down
neck is often called a "stargazer", and is often under-conditioned
because it is difficult for him to engage his hindquarters. Ewe necked horses
are frequently underweight and many have a bulging underline.
The horse with a large crest or "crest
fallen" neck is usually the product of obesity, which, of course, can be
corrected.
A bull neck is a heavy neck with a short upper
curve. Horses with this conformation generally work best in harness.
Horses with a swan neck--almost an
"S" like curve--never work well on the bit and often tuck their chins
to their chest. This neck generally has a long dip just in front of the
withers.
A naturally arched, well-defined neck is
suitable for any type of work.
THE BODY/WITHERS
When examining the horse’s body, begin with
the withers. The withers are formed by the coming together of the left and
right scapula, which don’t actually touch, but are held in place by muscles.
If the withers are rounded, flat and with
little definition, they are called "mutton withers." Mutton withers
affect all physical action and allow no free flow of movement. Saddles slip
easily on mutton withered horses.
High withered horses are hard to fit with a
saddle, but can generally perform any kind of work.
THE BACK
The horse’s back lies behind the withers and
to the loin, which is defined as the last rib to the point of the hip. The loin
is considered to be long if it is more than a hand’s length.
A hollow back looks concave and can be rider
induced due to a lack of drive from the hindquarters. Riding with incorrect
contact, a pull instead of a push, creates the low back and a strung out horse.
This condition is often seen in horses used for distance trail riding.
Short backed horses have limits to their
lateral flexion, and therefore generally lack suppleness.
A roach back--the spine raises in the loin
area--is often associated with stiffness in the back. Roach backed horses
cannot use their loin properly and so they are limited in quick lateral
movements.
Long backed horses generally have a weak loin
area. The weakness here precludes them from "folding" (drawing their
hind legs forward under them) quickly, so these horses lack both speed and
power.
A horse is said to have "rough
coupling" if he has any kind of a depression in his back just in front of
the croup. Rough coupling can be compensated for by being sure the horse is
very well conditioned.
THE CHEST
A horse with a wide chest can do just about
anything, but the width will often adversely affect the horse’s length of stride
and speed. Look for a horse with a chest proportional to his overall look. If
you immediately notice the horse has a wide chest, he probably has a little too
wide a chest.
RIBS
Standing in front and just a little to one
side of the horse, you should see "well-sprung" ribs, meaning the
ribs are prominent at the heart girth area. Well sprung ribs taper in as they
approach the horse’s flank.
Barrel ribs are prominent all the way to the
flank. The horse has a body "like a barrel." This width all the way
to the flank generally accounts for an uncomfortable ride, because the horse
cannot easily bring his hind feet well forward and under his body.
Pear shaped ribs are narrow at the heart girth
and widen toward the flank. A horse with pear shaped ribs should be used on
level terrain and cannot be expected to do a lot of work. As the barrel ribbed
horse, he cannot easily bring his hind legs forward.
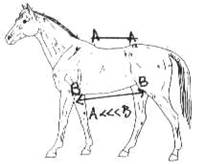
FRONT LEGS
Looking at the front legs from the front, you
should see the form of the bone entering the joints in the center.
A horse with a base narrow stance cannot be
expected to perform well in speed events or events which require athletic
agility.
Base wide horses are best suited for easy
pleasure riding.
Horses which toe-out can be used for high
impact events, while horses which toe-in should be used only in low impact
activities.
Move to the horse’s side to evaluate the
horse’s shoulder. An upright shoulder indicates the horse can work in sprint
activities. The horse’s speed lies in his ability to gather and get into the
next stride, not on the length of the stride. In other words, the more strides
within a particular distance, the more speed. A horse increases speed by
driving off the ground. His speed slows as he travels through the air.
If the horse has a sloping shoulder, his
withers will be well behind his elbow. Horses with this conformation are well
suited for jumping, dressage and driving.
A long arm produces speed, but is also
excellent for the dressage horse.
A short arm "from the point of the
shoulder to the elbow" will create an angle of less than 90 degrees.
A long forearm favors speed and jumping
ability. The horse with a short cannon will generally
have speed, agility and foreleg soundness.
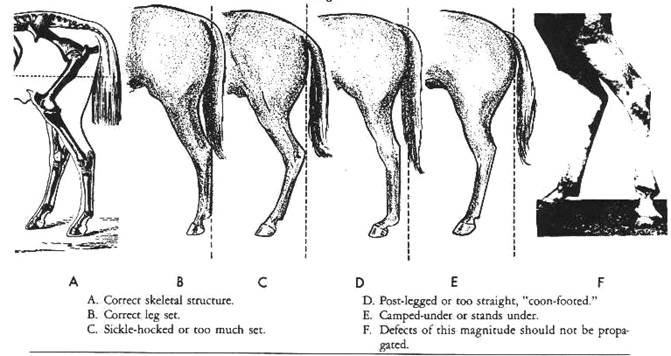
From the side you can determine whether or not
the horse is over at the knee or back at the knee. Back at the knee
conformation is frequently associated with unsoundness, but is also the desired
conformation for the modern western pleasure horse as he will move slowly with
flat knees and little reach.
Over at the knee horses are not pleasing to
look at, but many have speed and seem to remain sound.
Look at the horse from the front to see if the
horse has bench or offset knees. A horse is said to be bench kneed when the
forearm enters the knee to the left or right of where the cannon bone exits the
knee, making the forearm the back of the bench, the knee the bench seat and the
cannon the bench legs.
An offset knee has both the forearm and the
cannon entering and exiting the knee either on the medial or lateral side.
The fetlock joint should be clean and well
defined.
A horse with long pastern provides a smooth
ride and makes a nice pleasure horse or dressage horse.
Short pasterns contribute to a harder ride,
but also aid a horse’s speed.
HINDQUARTERS
Stand at the side of the horse to begin your
evaluation of his hindquarters.
The perfect length of the hindquarters is 30
per cent of the total body length and is measured from the point of the hip to
the point of the buttocks.
A short hindquarters
“less than 30 per cent of body length” is associated with a horse which lacks
speed and power. Remember, all action initiates in the hindquarters.
CROUP
A flat or horizontal croup is associated with
a flat pelvis. The topline of the horse continues all
the way to the dock of the tail. Horses with flat croups “which are quite
common” have a flowing stride at the trot. They are especially good at distance
trail riding, and driving in harness.
A steep rump is called a "goose"
rump and is not particularly common. Horses with a goose rump are best suited
for slower types of work, such as pleasure or trail riding. The steep slant of
the pelvis shortens the backward swing of the leg.
Narrow hips limit the amount of muscle the horse
can carry, thereby limiting the amount of muscle power possible.
A "knocked down" hip is when one hip
bone is lower than the other. The condition is fairly common. When examining
the horse from the rear, be sure to watch carefully as he is walked away from
you.
A long hip is easily recognized when the
stifle joint sits at or below the sheath line on a male horse. Low stifles are
particular good for horses which are intended for eventing
or show jumping.
A short hip creates a high stifle joint.
Horses with high stifles are best suited to draft work.
A short gaskin is associated with high hocks,
which generally means the horse will have inefficient movement, taking an extra
long stride.
High hocks make a horse suitable for trail, pleasure
riding, or driving.
A long gaskin is associated with low hocks
which often puts the horse in a camped-out position. Horses which are
camped-out behind lack power and smoothness. He can best be used as a trail
horse or pleasure horse.
The gaskin length is best when it sets the
hocks at the same level as the horse’s knees, for the horse will usually have
both power and speed. When evaluating the potential of a horse which will be
asked to work with speed and agility, look for hocks which are at the same
level as the knees.
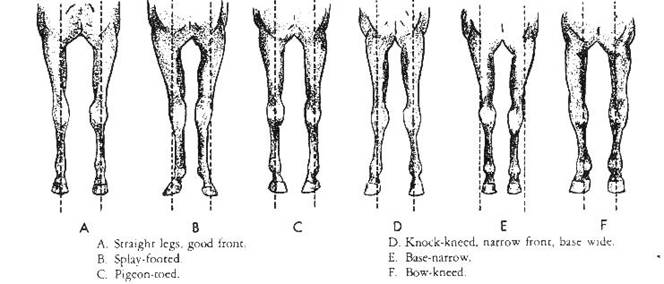
Sickle-hocked horses should not be considered
for speed events, while post-legged horses--very straight hind legs--are
particularly good at speed events, but little else.
A horse is said to be cow-hocked if when
viewed from behind the cannon bone and the fetlock joint are well to the
outside of the hocks.
If conformation is demanded in relationship to
efficiency of movement, a horse will tend toward a natural, but moderate,
cow-hocked stance. The horse’s toes should point outward, and he should NOT
stand square behind as virtually all conformational standards require.
When a horse increases his speed, the hips and
the hocks rotate outward, and the hoof rotates inward. A horse which stands
square behind naturally--and they are very, very rare--will strike his front
legs with his rear feet when he moves with speed.
Never allow a farrier to trim a horse’s hind
feet high on the inside to make the horse stand square behind.
Do not endorse breed association rules of
showing which allow a handler to "pull" the horse’s hocks out,
twisting the foot into a straight forward position. That is not the horse’s
conformation and it is ignoring the truth if it judged that way.
BALANCE
A horse is said to be balanced when his
withers and croup are level. A balanced horse is generally capable of working
any type of event.
Light boned horses should work low impact and
low speed events, while course boned horses are more suitable to high impact
events such as eventing.
The joints of both the hind and fore legs
should be clean and dry in appearance. Any puffiness or signs of fluid indicate
joint damage and eventual problems.
The pasterns, hind and fore, should be tight
and dry.
FINAL ANALYSIS
View the horse from the front, the side and
from behind, looking at the entire horse as a single object. Do you like what
you see? Is he smooth in overall appearance, or does some angle or roughness
jump out at you?
As you decide on the importance of each
conformation point you have viewed, evaluate you observations in relationship
to efficiency of movement, or to the work you want the horse to do.
Every horse can do everything and anything to
some degree. But mediocrity in performance seldom pleases the horseman. So it
is the responsibility of the horseman to understand how the form affects
function, and to select the correct conformation for the work to be done.
It is a bad horseman who demands a horse work
at an event for which he is not properly conformed.
Conformation is visible, but the thing which
makes performance champions cannot be seen. A horse’s heart to compete and win cannot be seen, but accounts for
‘super efforts’. Still, the horse moves
to into the winner’s circle on his physical conformation.
Quiz
Answer as True or False:
1. Breed associations establish
conformational standards.
2. Conformation standards assure the horse’s
soundness.
3. If the horse has good conformation, he’ll
be a great performer.
4. Judge conformation only as it relates to
efficiency of movement.
5. View a horse’s conformation from front,
side and rear.
6. A pretty head assures correct
conformation.
7. An upside-down neck is associated with a
high head.
8. High withers make saddle fit difficult.
9. A big, wide chest is very desirable.
10. A long
arm produces speed.
11. A
horse “over” at the knee is unsound.
12.
Short pasterns are bad.
13. The
perfect length of the hindquarters is 30% of the total body length.
14. A
short hip creates a high stifle.
15.
Horses are naturally slightly cow-hocked.
Assignment:
Please write a
conformation evaluation of the horse pictured.
Click
here for a conformation evaluation guide developed by Melinda Hertel, a professional certification student from
You will not be
able to get his actual measurements, but you can make pretty accurate
proportional approximations. Please
include angles, such as hoof, pastern, shoulder and hip; evaluate legs, joints
and feet for correctness.
Make a
conformation observation based on what you have learned, then
report how it may be a strength or a weakness for certain performances. Complete your report by suggesting a
discipline or disciplines for which you think this horse may be suited.
The horse
pictured is 4 years old, 16.1 hands and approximately 1200 pounds.
Click here to
view picture one – The Complete Horse, Left Side
Click here to
view picture two – The Complete Horse, Right Side
Click here
to view picture three – The Legs
Click here
to view picture four – The Front Legs and Chest
Click here
to view picture five – The Head
Click here to view picture six – The
Hindquarters
Please
e-mail all quiz answers to donblazer@horsecoursesonline.com
Include ‘Conformation Lesson One Quiz’ in the subject line.